1. Non-deadlock bugs
1.1 Atomicity-violation bugs
코드 영역은 원자성이지만 실행 중에는 원자성이 적용되지 않을 수도 있다.
= race conditon
-> mutex 로 해결 가능
1.2 Order-violation bugs
원하는대로 스레드가 실행되지 않아 오류가 생길 수 있다.
-> mutex랑 cond를 이용하여 해결 가능
2. Deadlock bugs
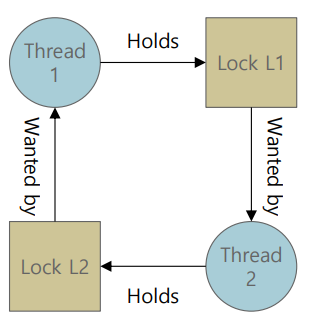
2.1 Conditions for Deadlock
- Mutual exclusion : 스레드가 lock 되어있어야 함
- Hold-and-wait : lock을 갖고 다른 lock을 갖는다
- No preemption : lock을 강제로 뺏지 못한다
- Circular wait : 각 스레드가 다른 스레드가 요청하는 lock을 보유하고 있다
-> 4개가 모두 충족되면 Deadlock 발생
2.2 Deadlock Solution ( Deadlock Prevention )
1) Mutual exclusion
atomic instruction 사용
int CompareAndSwap(int *address, int expected, int new) {
if (*address == expected) { //expected와 address 같으면
*address = new; //new 로 바꿔라
return 1; // success
}
return 0; // failure
}
// 활용
void AtomicIncrement(int *value, int amount) {
do {
int old = *value;
} while (CompareAndSwap(value, old, old + amount) == 0);
}위 함수를 활용하여 linked list에 노드를 삽입할 때 활용할 수 있다.
void insert(int value) {
node_t *n = malloc(sizeof(node_t));
assert(n != NULL);
n->value = value;
do {
n->next = head;
} while (CompareAndSwap(&head, n->next, n) == 0);
}
2) Hold-and-wait
lock이 여러개 있을 때 lock 전체를 mutex로 보호
이는 critical section이 커진다는 문제와 미리 lock을 다 알아야한다는 단점이 있음.
3) No preemption
top:
pthread_mutex_lock(L1);
if (pthread_mutex_trylock(L2) != 0) { //L2 실패하면
pthread_mutex_unlock(L1); // L1 도 포기하고 다시 처음으로 이동
goto top;
}pthread_mutex_trylock()를 이용하여 실패시 대기하지 않고 다른것을 시도하게 한다.
앞에 성공한 것들이 있어도 하나 실패하면 위에서 모두 포기하고 맨 위로 올라단다.
이는 잘못하면 모든 스레드가 실패해서 저기 안을 뱅뱅 돌 수 도 있음. 이는 goto 전에 랜덤 delay를 주는 방법도 있다.
4) Circular wait
여러가지 lock이 있을 때 모든 스레드가 똑같은 순서로 lock 해준다.
2.3 Deadlock Solution ( Deadlock Avoidance )
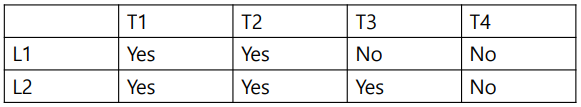
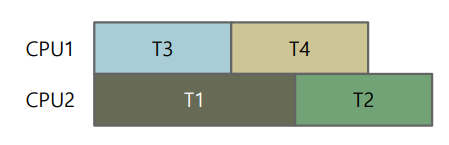
T3와 T4는 어떤 스레드와 같이 실행되도 문제되지 않는다. 따라서 아래 사진과 같이 계획 할 수 있다.
'학부 내용 정리 > [ 2-1 ] 운영체제' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [ OS ] Files and Directories (0) | 2022.06.14 |
|---|---|
| [ OS ] I/O Devices and HDD (0) | 2022.06.13 |
| [ OS ] Semaphores (0) | 2022.06.13 |
| [ OS ] Condition Variables (0) | 2022.06.12 |
| [ OS ] Lock-based Concurrent Data Structures (0) | 2022.06.12 |